问题描述
创建学生信息管理系统,具体要求如下:
学生信息包括:学号 姓名 数学成绩 英语成绩 计算机成绩
- 功能1:添加学生信息 执行1时,输入学号,姓名,三门科目成绩;如果添加学生成功则输出“Add success”,如果学生已存在则输出“Students already exist”
- 功能2:删除学生信息 执行2时,输入学号信息;如果学生不存在,输出“Students do not exist”,如果存在,则输出“Delete success”
- 功能3:更改学生成绩信息 执行3时,输入学号信息;如果学生不存在,输出“Students do not exist”,如果存在,输出“Update success”
- 功能4:显示学生平均分成绩 执行4时,输入学号信息;如果学生不存在,输出“Students do not exist”,如果存在,则输出学生信息,如下格式:其中平均分为三门科目相加除以3,保留一位小数,每行之间换行。
- Student ID:2019989890
- Name:Jerry
- Average Score:89.3
问题求解:
- 构建一个学生信息管理系统,实现上述功能。
- 输入数据:第一行为一个整数n(0<n<130),后边共n行,每一行表示执行一种功能。其中1,2,3,4分别对应执行上面4种功能,具体格式见输入样例。 测试用例保证:学号和名字均为长度不超过10的字符串,各门课成绩为0到100之间的整数。
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: automata), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of states at any given time.
The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a transition.
Example: coin-operated turnstile
An example of a simple mechanism that can be modeled by a state machine is a turnstile.


Considered as a state machine, the turnstile has two possible states: Locked and Unlocked.
The turnstile state machine can be represented by a state-transition table, showing for each possible state, the transitions between them (based upon the inputs given to the machine) and the outputs resulting from each input:
-
Current State Input Next State Output Locked coin Unlocked Unlocks the turnstile so that the customer can push through. push Locked None Unlocked coin Unlocked None push Locked When the customer has pushed through, locks the turnstile.
-
The turnstile state machine can also be represented by a directed graph called a state diagram (above). Each state is represented by a node (circle). Edges (arrows) show the transitions from one state to another. Each arrow is labeled with the input that triggers that transition. An input that doesn't cause a change of state (such as a coin input in the Unlocked state) is represented by a circular arrow returning to the original state. The arrow into the Locked node from the black dot indicates it is the initial state.
6-32 实验10_5_指针数组初步
已知一个总长度不超过10000的字符串,字符串中只包含大写字母“A—Z”、小写字母“a—z”和空格‘ ’。空格用于分割单词,空格的个数不超过1000个。你的任务是将字符串中用空格分隔的单词打印出来。 你要按照如下要求完成任务:
- 1.利用指针数组指向每个单词的开始位置。
- 2.把字符串中单词结束后的空格改为“\0”,然后使用指针数组将每个单词打印出来。
利用状态机建模求解
当我们扫描整个字符串时,当前查看的字符可能位于单词中,也可能位于间隔的空格上。因此,我们设计两个状态:
non-wordword
针对不同的状态,根据下一个输入的字符,可能会有状态的转移。比如:
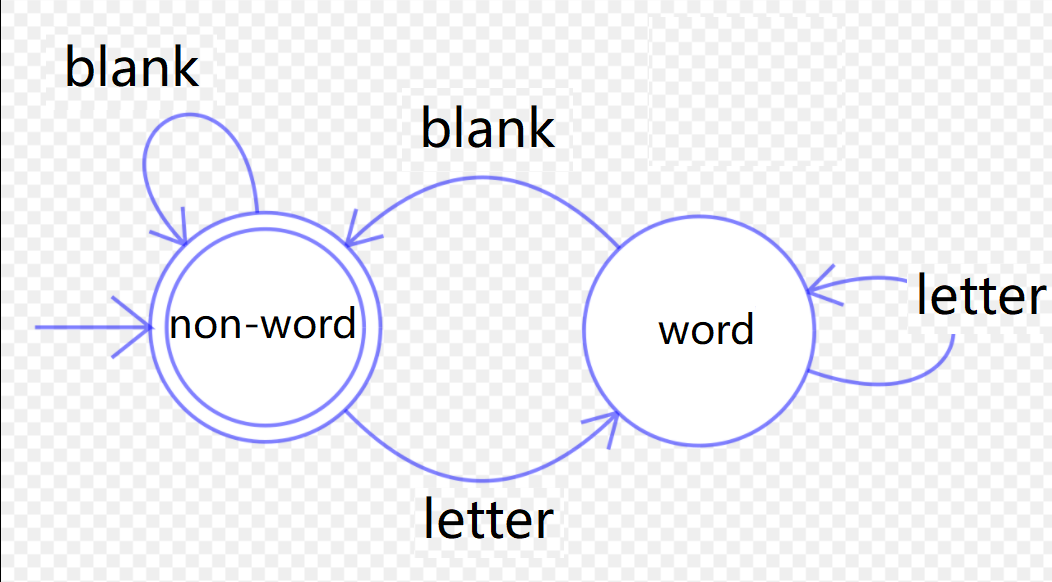
同时,在不同状态在遇到不同的输入字符时,还会有一定的输出以及action。具体:
-
Current State Input Next State Output non-word blank non-word Replace blank with a '\0' letter word A new word found, and to do something... word blank non-word Replace blank with a '\0' letter word None
-
状态机的初始状态是non-word。对于输入字符串中的每个字符,只要不是'\0',就运行上述状态机。也就是只要不是字符串的结尾'\0',就重复做计算。
getString函数如下:
int getString( char * source , char *strPtr[1000] )
{
int count = 0; // count the number of word in the string
int index = 0; // index for every word
int isWord = 0; // 0 means on state non-word, 1 means on state word
char *s = source;
while (*s != '\0')
{
if (isWord == 0)
{
if (*s == ' ')
{
*s = '\0';
}
else // in case of letter
{
isWord = 1;
strPtr[index] = s;
index++;
count++;
}
}
else // in case of state word
{
if (*s == ' ')
{
isWord = 0;
*s = '\0';
}
else // in case of letter
{
// nothing to do
}
}
// next character
s++;
}
return count;
}
代码中是以状态为主轴进行计算的。也可以做适当的合并处理,简化代码。
当需要对二维数组排序时,通常的排序需要移动大量的数据项。
为此,可以引入一个数组作为索引,只需要对此索引进行排序,不必移动任何数据项。
int a[5][3];
int b[5];
针对一维数组,原先需要交换数组a的元素,
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[i + 1] = temp;
如果是二维数组,则需要交换两行。
采用索引数组int b[5];只需要调整索引数组元素即可。
int temp = b[i];
b[i] = b[i + 1];
b[i + 1] = temp;
排序后,需要用b[i]代替a[i]中的i,即a[b[i]]。
int a[ROW][COLUMN];
对ROW行向量进行排序,用每个向量的第一个元素、或第二个元素作为键值进行排序。
代码参见:
https://onlinegdb.com/gCHibB-PS
每次交换时,需要交换整个向量。显然比较浪费。
设计另一个数组来存放这个二维数组的顺序。
大家可以在bubble排序中引入一个顺序数组试试。
Get a valid integer from keyboard.
It will check if there are non digits or too many digits.
https://onlinegdb.com/AvF3_-gE4
/*
Desc: Get a valid integer from keyboard.
It will check if there are non digits or too many digits.
A valid integer may include a sign and at most 9 digits.
Auth: Liutong XU
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAXCHARS 81
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
int getanInt();
int isValidInt(char val[MAXCHARS]);
int main()
{
int number;
number = getanInt();
printf("The number you entered is %d\n", number);
return 0;
}
int getanInt()
{
char value[MAXCHARS];
// typical scenario to use do-while
do
{
printf("Enter an integer, at most 9 digits plus one sign: ");
fgets(value, MAXCHARS, stdin);
} while (!isValidInt(value));
// while NOT valid, re-input. checking with a function
return (atoi(value));
// convert a string into a number, or you can write a piece of code to convert
}
int isValidInt(char val[MAXCHARS])
{
int start = 0;
int pos;
int valid = TRUE;
int sign = FALSE;
// empty string is NOT valid
if (val[0] == '\0' || val[0] == '\n')
return FALSE;
// we have a sign
if (val[0] == '-' || val[0] == '+')
{
sign = TRUE;
start = 1;
}
// a sign without any digit, invalid
if (sign == TRUE && val[1] == '\0' && val[1] == '\n')
return FALSE;
// now start processing digits
pos = start;
while (valid == TRUE && val[pos] != '\0' && val[pos] != '\n')
{
if (val[pos] < '0' || val[pos] > '9') // non-digit
valid = FALSE;
pos++;
}
// too many digits CANNOT fit into an int type
if (pos - sign > 9)
{
valid = FALSE;
printf("Too many digits...");
}
// print a message
if (!valid)
{
printf("Invalid integer\n");
}
return valid;
}
Determine whether str2 is a substring str1
substr(str1, str2)
We could use two pointers or indices point to head and tail of the string respectively.
Algorithm
While head is less than tail,
swapping the head and tail elements, narrowing the head and tail, and repeat the process.
String inserting/deleting are similar to integer array shifting, because strings are arrays of char.
This time, we will insert or delete more than one charactes.
Length of String
Because strings are ending with a '\0', just searching '\0' in a string and the index of '\0' is same as the number of charaters before '\0'.
Use two-dimensional array to store students's scores of several courses.
int studentGrades[STUDENTS][COURSES];
Page 1 of 5
