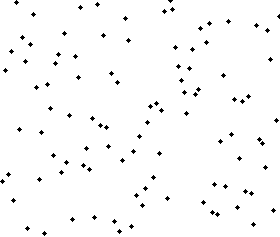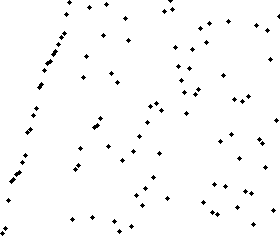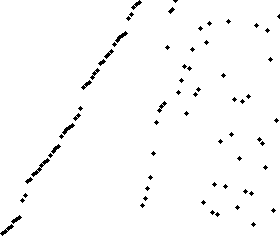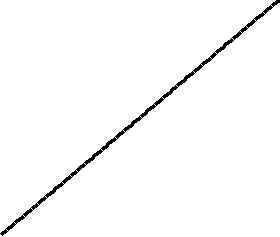
Bubble sort
Bubble sort, sometimes referred to as sinking sort, is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list to be sorted, compares each pair of adjacent items and swapsthem if they are in the wrong order. The pass through the list is repeated until no swaps are needed, which indicates that the list is sorted. The algorithm, which is a comparison sort, is named for the way smaller or larger elements "bubble" to the top of the list. Although the algorithm is simple, it is too slow and impractical for most problems even when compared to insertion sort.[2] It can be practical if the input is usually in sorted order but may occasionally have some out-of-order elements nearly in position.

selection sort
In computer science, selection sort is a sorting algorithm, specifically an in-place comparison sort. It has O(n2) time complexity, making it inefficient on large lists, and generally performs worse than the similar insertion sort. Selection sort is noted for its simplicity, and it has performance advantages over more complicated algorithms in certain situations, particularly where auxiliary memory is limited.
The algorithm divides the input list into two parts: the sublist of items already sorted, which is built up from left to right at the front (left) of the list, and the sublist of items remaining to be sorted that occupy the rest of the list. Initially, the sorted sublist is empty and the unsorted sublist is the entire input list. The algorithm proceeds by finding the smallest (or largest, depending on sorting order) element in the unsorted sublist, exchanging (swapping) it with the leftmost unsorted element (putting it in sorted order), and moving the sublist boundaries one element to the right.

Insertion sort
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time. It is much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort.
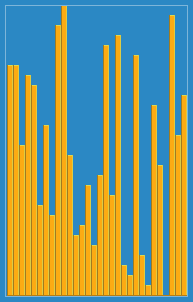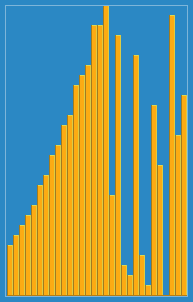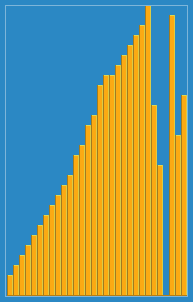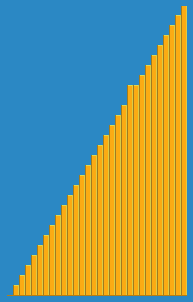
merge sort
In computer science, merge sort (also commonly spelled mergesort) is an efficient, general-purpose, comparison-basedsorting algorithm. Most implementations produce a stable sort, which means that the implementation preserves the input order of equalelements in the sorted output. Mergesort is a divide and conquer algorithm that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945.