Boolean algebra has been fundamental in the development of digital electronics, and is provided for in all modern programming languages. It is also used in set theory and statistics.
Value
In Boolean algebra they denote the truth values false and true. These values are represented with the bits (or binary digits), namely 0 and 1.
Basic Operations
AND (conjunction), OR (disjunction), NOT (negation),
|
|
开关
两个状态,开,关。
操作开关,改变状态。
Representation:
开,高电压,逻辑1
关,低电压,逻辑0
操作方式:手工—>机械—>机电—>电子
Switching circuit theory provided the mathematical foundations and tools for digital system design in almost all areas of modern technology.
From 1934 to 1936, NEC engineer Akira Nakashima published a series of papers showing that the two-valued Boolean algebra, which he discovered independently, can describe the operation of switching circuits. His work was later cited and elaborated on in Claude Shannon's seminal 1938 paper "A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits". The principles of Boolean algebra are applied to switches, providing mathematical tools for analysis and synthesis of any switching system.
Logic gate
| AND Gate | 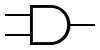 |
 |
| OR Gate | 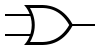 |
 |
| NOT Gate / Inverter | 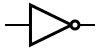 |
 |
The XOR gate (sometimes EOR gate, or EXOR gate and pronounced as Exclusive OR gate) is a digital logic gate that gives a true (1/HIGH) output when the number of true inputs is odd.
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
| A | B | A XOR B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
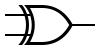 |
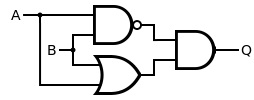 |
