An adder is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of processorsadders are used in the arithmetic logic units.
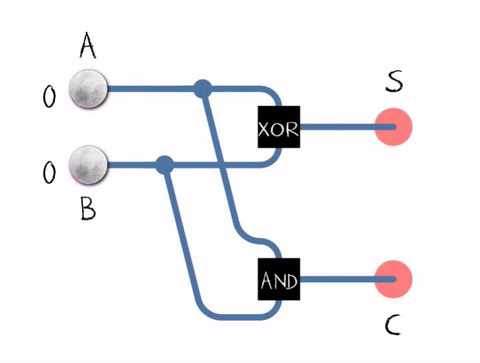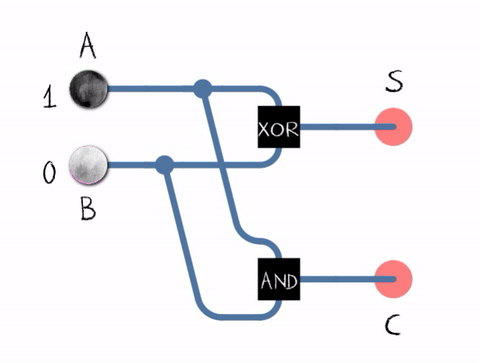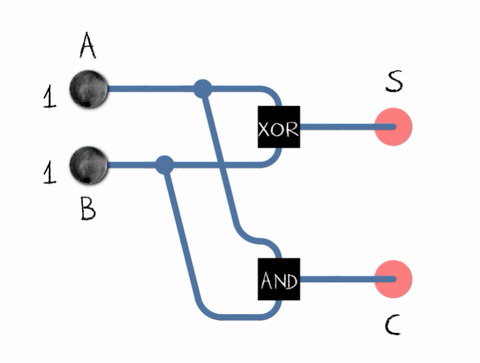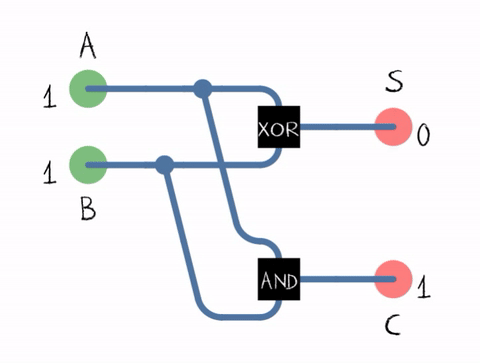
The half adderadds two single binary digits A and B. It has two outputs, sum (S) and carry (C). The carry signal represents an overflow into the next digit of a multi-digit addition.
Half adder logic diagram

Half adder in action
A full adder adds binary numbers and accounts for values carried in as well as out. A one-bit full adder adds three one-bit numbers, often written as A, B, and Cin; A and B are the operands, and Cin is a bit carried in from the previous less-significant stage. The full adder is usually a component in a cascade of adders, which add 8, 16, 32, etc. bit binary numbers.
Logic diagram for a full adder.

Full adder in action. A full adder gives the number of 1s in the input in binary representation.
Schematic symbol for a 1-bit full adder with Cin and Cout drawn on sides of block to emphasize their use in a multi-bit adder

